
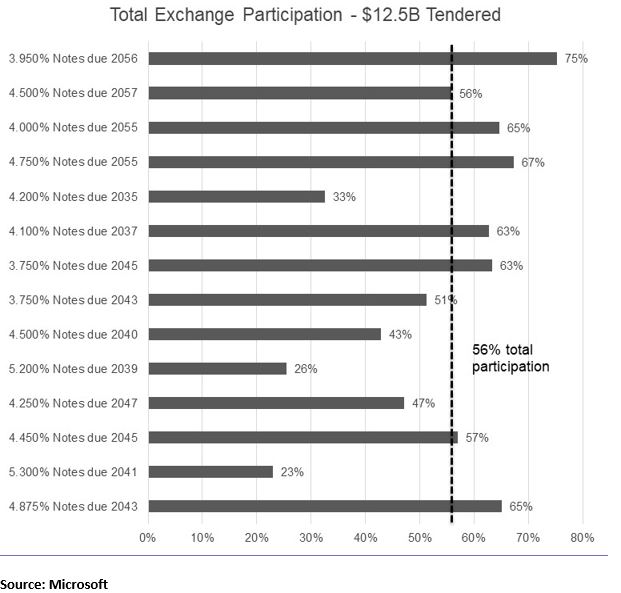
Liability management success: Microsoft received exchange interest of $12.5B, 56% of the targeted notional amount.
Treasury teams managing their debt portfolios have a menu of liability management transactions to choose from, including bond tenders, open-market repurchases, consent solicitations and debt exchanges. To use most of these tools, corporates need to offer investors a reasonable amount of time to decide, ranging from five to 20 business days.
- So a successful liability transaction such as a debt exchange depends, in part, on a generally stable underlying market. COVID-19, of course, wreaked havoc on markets and sent volatility levels spiking. But monetary actions by the Fed and fiscal stimulus help calm markets, resulting in a sharp drop in volatility. And that opened the door for companies including Microsoft to take action.
Laying the foundation. At a recent NeuGroup for Capital Markets office hours session, Microsoft’s treasury team discussed their recent debt exchange, announced on April 30, 2020 and settled on June 1, 2020.
- Like any successful capital markets transaction, the preparation done in the months before by the treasury team laid the foundation for a debt exchange which accomplished the company’s financial and strategic objectives.
- These objectives were driven by the primary principle to maximize economic value, including reducing the annual interest rate paid and being P&L accretive.
Debt exchange details. On April 30, the company announced a registered waterfall exchange offer targeting 14 series of notes across two separate pools with maturities between 2035-2057, all with coupon rates above 3.75% (the existing notes) in exchange for cash into $6.25 billion of new notes due 2050 and $3 billion of new notes due 2060.
- Microsoft set a waterfall prioritization based on economic value and registered the exchange via an S-4 filing requiring a 20-day offering period. It included an early exchange time on May 13, 2020 which offered investors better economics by exchanging their notes earlier than the official expiration date on May 28, 2020.
- The strong interest by investors in the exchange allowed Microsoft to increase the amount of the new 2060 note to $3.75 billion. The final coupons on the new 2050 notes and the new 2060 notes were 2.525% and 2.675%, respectively.
Banks with strong LM credentials. Working with joint dealer managers, Microsoft was able to tap into the knowledge and insights of two banks with strong credentials in liability management.
- These banks were able to form a consensus on important details including what spreads over US Treasuries to use for both the existing notes and the new notes, modeling analysis, supporting logistics, the identification of holders of the existing notes and their likelihood of participating in the exchange, and potential ways to hedge interest rate movements.
- At the end of the day, the transaction generated significant interest savings, and extended Microsoft’s debt maturity profile. The exchange also established new, liquid, par securities by allowing investors to move out of high dollar-priced bond issues.


